Microeconomics studies what is going to happen in an economy when individuals make a decision. An individual makes choices when there are changes in price, mode of production etc. The individuals are divided into buyers, sellers, business owners in the economy. As a result, these groups create the market forces in the economy like demand and supply. Microeconomics studies the decisions of individuals in the economy for proper allocation of resources.
The primary task of microeconomics is to study prices and production in the market. There is an interaction between the different markets in the economy.

The study of interaction between markets is under the realm of microeconomics. But the economy wide aggregate is the study of macroeconomics. As a result, the scope of microeconomics is to study the market from the individualistic point of view.
Microeconomics studies the allocation of resources in the economy. The change in allocation of resources in the economy lead to change in the combination of production of goods and services. Microeconomics studies the basic two problems faced in the economy.
Due to change in allocation of resources the distribution of goods and services change in the economy.
Resources are scarce. As a result the limited resources have to be distributed equally in the economy.
Microeconomics Definition
Microeconomics gives a detailed view about the economy. It studies the implications of various economic decisions on the economy. As a result why different goods have different values in the market. Business productions and benefits that are accrued is under the realm of microeconomics. The interaction between different markets in the economy and the individuals is the study of microeconomics. Therefore, you can say microeconomics is a social science that studies the production of goods and services in the economy and its distribution.
History
Alfred Marshall is considered the father of Microeconomics. This approach of economics helps to understand the practical working of the economy. As a result, it focuses on the issues that affect individuals and companies in the economy. Microeconomics is the study of individuals, households and firms behaviour in decision making and allocating resources in the economy. It helps in providing various economic policies that facilitate the easy formulation of economic strategies.

Microeconomics helps in studying the conditions of economic welfare. Because it helps to understand the standard of living of the people in the economy. This branch of economics helps us understand the level of satisfaction derived by the people in the economy after consumption of different goods and services. Since, proper allocation of resources helps to increase the productivity of the resources. As a result the efficiency of the resources also increases.
Central Problems of an Economy
The basic economic activities are production, consumption and exchange of goods and services. The problems that are faced in the economy with resources is that of scarcity. Because resources are scarce in nature. At the same time, since resources are scarce there is a problem of choice. Basically the two main central problems are scarcity and choice. But the two problems give way to important questions. [Source- Your Article Library]
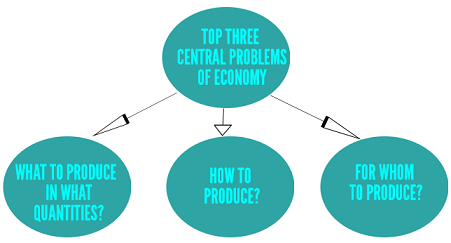
What is produced and in what quantities?
One of the central questions for microeconomics in the economy is what is to be produced and in what quantity. Because the resources are scarce in nature, the production should be in the appropriate quantity. Secondly what is to be produced i.e. the choice of goods that is important for the economy. The economy faces problems whether to produce food or clothing or something else. The choice between consumption goods or investment goods to increase production and consumption. It is on the society to decide the answers to these questions.
How are these goods produced?
There are four factors of production i.e. land, labour, capital and entrepreneur. The society must decide which resources i.e. labour or capital is to be used to produce goods and services in the economy.
For whom these goods are produced?
This question arises regarding the distribution of goods and services in the economy. The economy needs to ensure the equal distribution of goods for every person.
Thus, every economy in the world faces the two problems that microeconomics chooses to answer. The central pillars of microeconomics is the allocation of scarce resources and the fair distribution of the goods and services.
Organization of Economic Activities
The basic problems regarding production and distribution have to be answered. Because these problems pose a threat for the economy. As a result, the basic problems need to be addressed. The problem can be solved by free interaction of the individuals in the market or by central authority that is the government.
Centrally Planned Economy in Microeconomics
The activities are planned by the government or a central authority. As a result, the decision of production and distribution depends upon the government of that country. It is on the government to decide the allocation of resources. For example, education, social development etc. Education, social development enhance growth in the economy. In case, when distribution of goods and services are not equitable in manner, then the government can easily intervene.
Market Economy in Microeconomics
In this type of economy all the activities are organized through the market. The market forces play a major role in this type of an economy. As a result pricing of the commodities needs to be managed. In this economy the goods and services come with a price. The price is the value of the goods and services in the market. The price of the products depend on the market forces i.e. demand and supply. Any change in the market forces will create a change in the prices of the goods and services in the company.
Market plays an important role in microeconomics. Market is where buyers and sellers meet. Business transactions take place in a market. From this place the distribution also takes place. Microeconomics is the study of production and distribution in the economy. Market plays the key role in this type of economy.
There are different branches of microeconomics. Consumer theory is the branch of microeconomics that deals with household behaviour. But, consumer theory is on the concept of utility.
Microeconomics Concept
Microeconomics studies the allocation of resources in the economy. Proper allocation of resources ensures the productivity of resources. As a result, the efficiency in the economy will also increase.
Utility in Microeconomics
Utility is a very important concept in microeconomics. It is the satisfaction that is derived after the consumption of a particular product. Utility is the want satisfying capacity of a particular product. Therefore, utility depends on the need of the product. As a result the more the need of the product the more will be the desire to have the product. As a result the utility of the commodity will be high.
In economics, utility is a subjective concept. It depends on the individual who is consuming the product. Different people will have different utilities for the same product. Because the desire or need of the product is different. Every individual has his own choice. Choices of a person change.
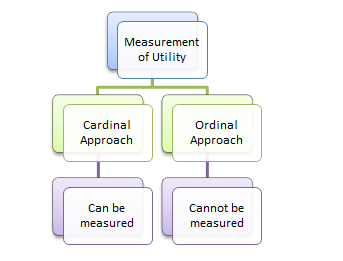
Measures of Utility
There are different measures of utility. Cardinal utility analysis assumes the level of utility to be expressed in numbers.
Total Utility
Total utility is the total satisfaction derived after consuming that article. The more a person consumes the product the higher will be the satisfaction level of the consumer. It increases after each consumption.
Marginal Utility
Marginal utility is a totally separate concept of microeconomics. It is the change in total utility after consumption of one additional unit of the commodity. Suppose 4 apples give 28 units of utility and 5 apples give 30 units of utility therefore the marginal utility is 2. [Source- Britannica]
Therefore it is said that the sum total of marginal utility of all the consumption units is total utility that is derived.
Types of Utility in Microeconomics
Utility is the usefulness of the product experienced by the consumer. Therefore, companies try to increase the utility of products to increase customer satisfaction and sales. The concept of utility comes under behavioural economics. There are four types of utility in microeconomics.
Form Utility
The shape or form of a product when changed creates form utility in the economy. For example, furniture is made of wood and steel is used to make cabinets. As a result by changing the structure of a material a product is being built.
Place Utility
Transporting a commodity from one place to another creates place utility. The transport services help to create place utility in the market.
Time Utility
Storage of products for a longer period of time in the economy creates time utility in the economy. Traders hoard products to make them available during the time of crisis. As a result, traders earn higher profits by selling the products.
Service Utility
The service of doctors, lawyers create service utility. They provide their services to different people to create utility in the economy.
Features of Utility
Utility of a product or service in the economy has different features. These features of utility in microeconomics helps to analyse the economy. [Source- Economics Discussion]
- Utility has no real moral or ethical significance. It is purely a behavioural concept. As a result, utility derived from consuming a product may be different depending upon the person.
- It is a psychological concept. Utility is the satisfaction derived by consuming a product of your own choice. Satisfaction for the product depends upon the psyche of the person.
- Utility derived after consuming a product varies from person to person. Therefore utility is totally an individual concept. As a result it is also a relative. Because the utility of a product may vary from one person to the other.
- Utility is not an objective concept. It is a subjective concept. Because the level of satisfaction cannot be measured numerically. As a result, the level of utility cannot be measured cardinally or numerically.
- Utility for a product depends upon the intensity of want. The higher the need/want, utility will be high. Utility and want are directly proportional. Utility is a function of the intensity of want in the economy. At the same time, if the person is satisfied, then the utility derived from further consumption will be less.
Law of Diminishing Returns
The law of diminishing returns operates in the short run. It studies the change in output when the quantity of one input is changed. The law of diminishing returns states that when more units of a variable input is employed the total output will increase at an increasing rate then at a constant rate and eventually at a diminishing rate.
Assumptions
The assumptions of law of diminishing returns in microeconomics are
- The variable input is labour in the economy.
- Capital is the constant factor of production.
- Fixed state of technology
- Fixed input prices.
Significance for Microeconomics
There are practical situations where this law is applied. Law of diminishing returns is not applied in every situation. Therefore, the application of the law of diminishing returns works majorly in agricultural production. The working of this law in industrial production is negligible. Because in agriculture the inputs are natural. But in the case of industrial production the inputs are man-made. As a result if variable inputs are applied the marginal returns starts to decline.
The law of diminishing returns helps to analyse the optimum amount of labour required to produce maximum output in the economy. The graph helps you to understand the optimal capital-labour ratio.
Causes
The causes of operation of law of diminishing returns are mainly.
Fixed Factors of Production
Fixed factors of production is an important cause of law of diminishing returns. Capital is the fixed factor of production.
Production is the result of the effective combination of factors of production. As a result every factor has to be increased for obtaining optimal production levels in the economy. There should not be any disturbance in the distribution of factors of production. As a result the production will not increase at an increasing rate. As a result the law of diminishing returns will apply in the economy.
Factors of Production are Scarce
The factors of production are scarce in nature in the economy. Due to scarcity of resources in the economy, sometimes the factors of production cannot be increased. The output maximization is not possible in such a situation.
Lack of Perfect Substitutes
The factors of production do not have a substitute in the economy. Law of diminishing returns does not apply due to the lack of perfect substitutes of the factors of production.
Optimum Production
The proper adjustment of the factors of production will yield optimal production level in the economy. The economy reaches the optimal production level after employing the factors of production. But, by applying variable factors of production the marginal product will decline. As a result this will help to operate the law of diminishing returns.
Limitations of Law of Diminishing Returns in Microeconomics
According to Alfred Marshall, the law of diminishing returns has universal application in the economy. This concept is important in microeconomics. But there are certain limitations though. [Source- Economics Discussion]
- When land is new in the economy it will deliver better yield with the application of factors of production. The returns will be more as productivity is high. As a result the marginal returns will increase instead of decreasing.
- The unavailability of capital resources ensure the employment of capital to be less. Capital helps to increase the production in the economy. As a result, the marginal product will increase instead of decreasing.
- Technological improvements help in increasing the production of goods and services. Therefore, the productivity also increases. As a result the marginal product will increase instead of diminishing.
Market Structure
Market structure is the environment where a firm buys and sells its products and services. Thus, number of firms is an important feature of market structure in the economy. The second criteria is the ease of entry and exit from the market. The third criteria is the degree of product differentiation. As a result the market structure forms an important part of microeconomics.

Perfect Competition
Perfect competition has large number of buyers and sellers in the market. At the same time the goods available in the market are relatively the same. The most important feature of perfect competition is the free entry and exit of the firms.
The price level remains the same in this type of market structure. As a result constant prices do not have a great effect on the profits of the firm. The buyers and sellers in this market agree to take on the price determined by the market forces. Therefore the market price of the products are relatively the same.
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is the market structure where there are large numbers of small firms. The main difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition is in perfect competition the products are relatively the same. Therefore, heterogenous products are an important feature of monopolistic competition. As a result the firms can exert some control over the prices.
The assumptions of monopolistic competition market structure are that all firms maximize profits. Free entry and exit is the second assumption of monopolistic competition. One of the key assumptions is that in this form of market the sellers sell differentiated products. The customer preference is important while selling a particular product. However this type of market structure does not exist as firms try to influence the price of the product.
Oligopoly
Oligopoly market dominated by a small number of firms. The level of competition in the market is relatively less. The firms in this type of market structure either compete against each other or collaborate with each other. This form of collaboration leads to higher price levels in the economy. When the price of commodities rise, the profits of these firms will also increase.
The assumptions of the oligopolistic competition are that all firms in this market structure try to maximize their profits. The firms in this market structure decide the prices of the goods and services in the market. The products sold in this market are homogenous or heterogenous in nature. The important feature of the market is that there is a barrier to entry and exit in this form of market. The firms in the market are relatively low. As a result, three to five firms dominate this type of market. One of the most important examples of oligopoly is in the market for gaming consoles. Sony, Microsoft and Nintendo dominate the market.
Monopoly
Monopoly is the market structure where only one firm dominates the market. The market power exerted is the highest. Therefore, the prices of products in this form of market is dominated by the single firm. As a result the prices are high in this form of market. The profit earned by the firm is also high. [Source- Lumen Learning]
The firm decides the price level in monopoly form of market structure. There are barriers to entry and exit in this form of market. Thus, the primary motive of the seller is to maximize the profit.
From the economic perspective it is not desirable to have monopolies. Thus, the output generated in the monopoly form of the market is high. But the price of these goods produced are relatively high. As a result there is government intervention in this form of market.
Conclusion
In this part, we got an abstract understanding about the some pillars of microeconomics. Thus, now we understand what are some of the central concepts of microeconomics. In this part, we study about utility, market structure and law of diminishing returns. At the same time, we see the central questions of the economy. In part II we will see the other concepts of microeconomics. Read Well and Study Hard!


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp