The law of demand is one of the important concepts in economics. This explains how in a market allocation of resources takes place. As a result the determination of the price of goods and services also takes place with the interference of the market forces. The law of demand has an inverse relationship between the price of the commodity and the quantity demanded. The main reason behind this inverse relationship is diminishing marginal utility. Here is our 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand.

Economics studies how people use limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants. The focus of the law of demand is on the unlimited wants that arise in the economy. The law of demand focuses on the factors that cause a change in the demand of quantity consumed in the economy. Demand and supply are the market forces that operate in the economy. In the free market economy, these market forces play a crucial role in regulating the prices.
Demand – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
Demand refers to the commodity that a buyer wants to purchase backed by purchasing power. Here the main keywords are want and purchasing power. For demand to complete in the economy only want cannot be the factor. It has to be backed by purchasing power of the commodity. Because demand will be complete if the commodity is transferred from the seller to the buyer after paying the price of that commodity.
Demand theory in the economy is the basis of the law of demand and the demand curve. It states the relation between the customer desire and the amount of goods that are available. The main concepts of demand are desire, willingness and the price to pay for the product. All the three concepts are interconnected. Demand as a concept focuses on all the three heads. Because they are interconnected, demand will not be complete if one is missing.
As a consumer of the product the foremost important part of demand is desire for a certain product. Desire is the want that arises after seeing a product in the market. Willingness for the product is second. Because the desire is affirmative there has to be willingness to purchase the product. The third concept is very important i.e. price to pay. If the buyer does not have the purchasing power then the demand will not be complete. As a result, the demand becomes complete if all three concepts fall in line in the economy.
Demand Curve – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
It is the graphical representation of the relation between price of commodities and quantity demanded in the economy. The price of the commodity is marked on the Y-axis. The quantity demanded is marked on the X-axis. The graph represents the inverse relation between price and quantity demanded.
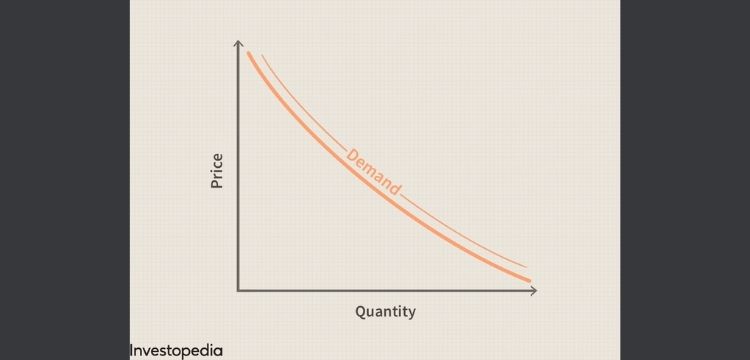
The demand curve is downward sloping as it shows the negative relationship between price and quantity demanded.
• Suggested Blog: WHAT IS MACROECONOMICS – LEARN IN 10 MINUTES
Law of Demand – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
The law of demand states that when the price of the commodity increases the quantity demanded will decrease. The law of demand states the inverse relation between the two attributes in the economy.
When the price of goods and services increase the demand for the commodity decreases. But when the price of goods and services decrease the demand for the commodity increases in the economy.
Demand and Quantity Demanded
Change in demand refers to the shift of demand curve towards the right or left. A rightward shift of demand curve refers to the increase in demand. A leftward shift of demand curve refers to decrease in demand. Increase and decrease in demand is due to many factors in the economy. Change in demand induces the change in law of demand in the economy. Change in quantity demanded refers to change in position along the demand curve. With increase or decrease in price the quantity demanded along the demand curve changes.
This induces the law of demand also. The law of demand states that when price increases the quantity demanded decreases. And when price decreases the quantity demanded decreases. In this case the change is marked along the demand curve. Demand curve is downward sloping. The reason being the negative or the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. As the law of demand states now let us see the reason or the factors that affect the demand in the economy.
Elasticity of Demand – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
The elasticity of demand is an important concept in economics. Elasticity of law of demand can be classified into elastic demand, inelastic demand and unitary demand.
Elastic Demand
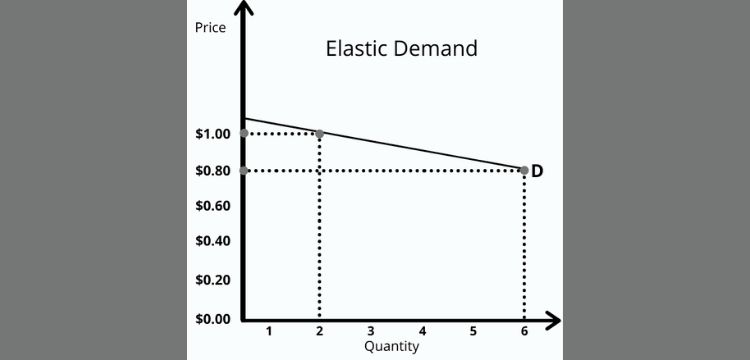
Elastic demand refers to when the change in quantity demanded is more than the change in price level in the market. With a small change in price in the economy the quantity demanded change is more. Consumer durable goods have elastic demand. The examples of consumer durables are fridge, washing machines etc. If the price increases for these products then the demand to purchase them will postpone.
Close substitutes goods also affect the elasticity of demand. If the price increases for a product then the consumer will shift to another commodity in the market.
Inelastic Demand
Inelastic demand refers to when the price change of the commodity in the market is higher than the change in quantity demanded. Quantity demanded of the commodity does not change much as compared to the price of the commodity. An example of inelastic demand is that of food grains. If the prices of food grains increase then the demand for the same will not decrease. The consumption of food remains the same irrespective of the rise in price.
Unitary Elastic Demand
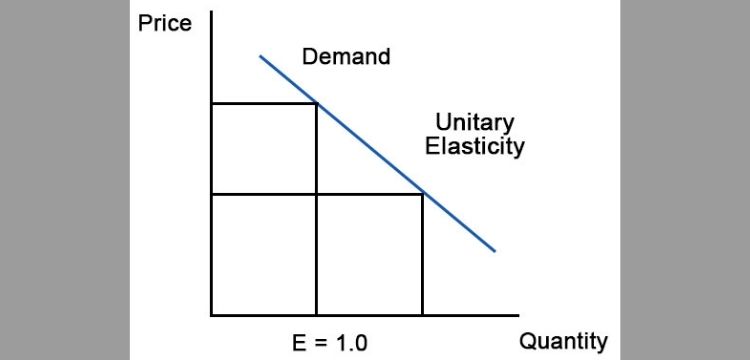
When the elasticity of demand is equal to one then the demand curve is unitary elastic. In this case, the change in price and change in quantity demanded is the same. An example of unitary elastic demand is digital cameras. When the price of a digital camera decreases by 10% then the quantity demanded of the same increases by 10% in the economy.
Factors affecting Law of Demand
Demand for a commodity in the market depends upon many factors. Price, income, prices of related goods all affect the law of demand in some way or the other.
Price – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
The price of a product affects the demand for the commodity in the market. When the price of a product is high then the quantity demanded will be low. As a result, there will be a shift along the demand curve. When the price of a product is low then the quantity demanded will be high. In this case, too there will be a shift along the demand curve. The law of demand also states that when price increases the quantity demanded declines.
Income – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
Income of a consumer also changes the level of demand in the economy. When the income of the consumer rises then the demand for goods and services in the economy increases. This will shift the demand curve rightwards indicating that the demand has increased. When the income level of the consumer decreases then the demand for commodities decreases. The demand curve shifts leftwards indicating that the demand for goods and services have decreased.
Price of Related Goods – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
Prices of related goods affect demand in a drastic way. Related goods can be substitute goods or complementary goods. When prices of certain goods change it affects the demand for other goods as well.
In the case of substitute goods, if the price of a commodity increases, the demand for the substitute good will increase. For example tea and coffee are substitute goods. When the price of tea increases then the demand for coffee in the market will rise. Because the price of tea is higher than the price of coffee.
In the case of complementary goods, the demand for the product will depend on the prices of the commodity. For example, cars and petrol are two complementary goods. If prices of petrol increase the demand for cars will decrease.
Taste and Preference – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
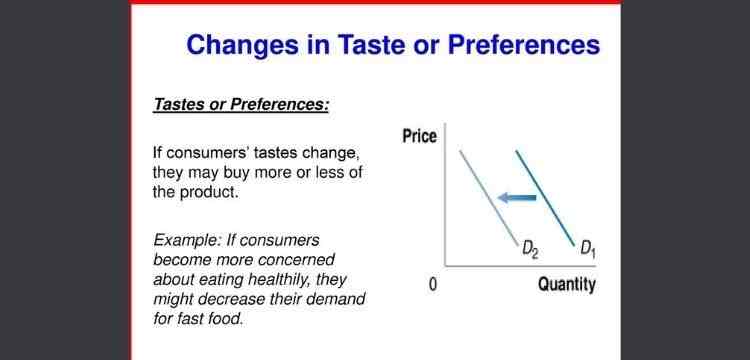
The taste and preference of the customers related to the choice of goods matter in the economy. The taste and preference for a product is a personal affair. As a result it depends on the psyche of the person. Taste and preference changes from time to time. If the preference for a product changes then the demand for that quantity will increase or decrease. Preference for a product depends on various factors like price of the commodity or the income of the person. If the price increases then the customer will prefer another product. If the income of the consumer increases then he will prefer luxury goods rather than inferior goods.
Expectations in change of price
Another factor that affects the law of demand is the expectation of rise in price of the product. A consumer will increase the demand for the product if he expects the price of the commodity to rise. This fluctuation in demand in the market will automatically cause a rise in price level due to the interaction of the market forces.
• Suggested Blog: WHAT IS MONETARY POLICY? Learn in 5 minutes
Causes of Law of Demand – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of that commodity causes the demand curve to slope downwards from left to right. The reasons behind law of demand are
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that when more and more units of a commodity is consumed the utility that is derived from the consumption of the successive units decreases. Therefore you can say that the law of demand depends upon the utility. If the level of satisfaction of the user is high then the demand for the product will be high. But since the price of the commodity remains constant the consumer will not be willing to pay the same price. As a result when the price of the product decreases the buyer will tend to purchase more of the product. The basic operation behind law of demand is that of diminishing marginal utility.
Substitution Effect
The substitution effect is substituting a product in place of another when the price of the product falls. When the price of a substitute commodity increase then the customer will prefer the given commodity as it is relatively cheaper. The example of a substitute commodity is tea and coffee. When the price of coffee increases then the demand for tea will increase. Because it is relatively cheaper as compared to coffee.
Income Effect
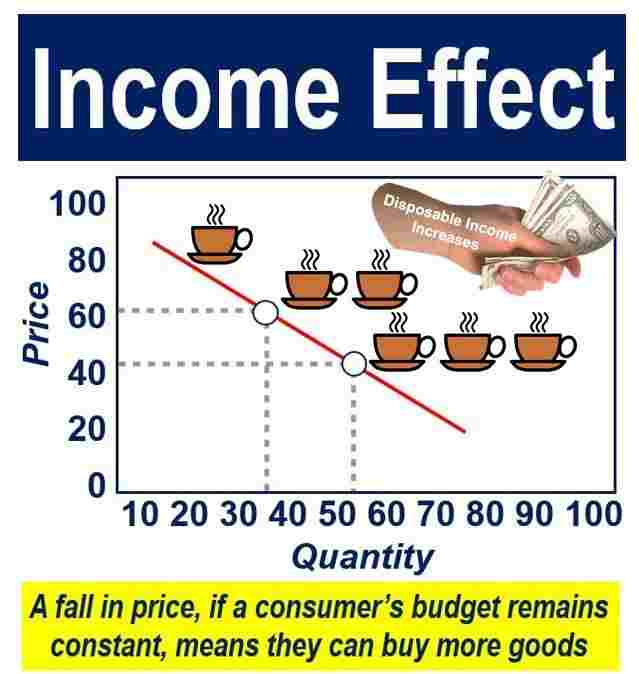
It refers to the effect on demand of a commodity when real income of the customer changes due to the change in price level. If the price of the commodity decreases then the purchasing power of the customer will increase. Purchasing power is the income effect.
Additional Customers
When the price of goods and services decrease there will be an addition to the total base of the customer. As a result, the number of customers in the market who want to buy the product will increase. Because there is a decrease in the price level of the product. As a result, old customers who were demanding the product will also increase their demand/purchase of the product due to the low price.
Exceptions to the law of demand – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
As the law of demand states that when the price of a commodity increases the demand for the commodity will decrease. But there are certain exceptions to the rule in certain cases. As a result in these cases the law of demand does not work efficiently. Because with change in price or income of the consumer the demand for these goods will decrease, increase or there will be no change.

Necessary Goods
Necessary goods are those goods that are consumed daily or it is used for daily household purpose. Salt is the best example of necessary goods in the economy. In this case if the income of the consumer increases then the quantity demanded of salt will remain the same. At the same time if the price of salt increases then also the quantity demanded will remain the same. Therefore in the case for necessary goods the price or income of the customer does not affect the demand for the product. It will remain the same.
Giffen Goods
Giffen goods are the inferior goods in the economy. In case for inferior goods the price or income of the customer does not matter. If the price of the inferior goods rise then there will be no effect on the quantity demanded of the commodities. At the same time, when prices of inferior goods decrease the effect on quantity demanded will remain the same.
When income of the consumer increases then the quantity demanded of the commodity will decrease. The law of demand in this case does not hold true. As a result with increased income the demand for these products decrease.
Veblen Goods
Economist Thorstein Veblen gave the concept of Veblen goods in the economy. This concept works on the principle of conspicuous consumption. In these cases as the prices of goods increase the demand for the commodities will also increase. Gold is an example of Veblen goods. In the market when the price of gold increases then the market demand of gold will also increase. The law of demand does not function in cases of Veblen goods.
• Suggested Blog: Guide To Research Paper Writing | Write A Research Paper
Conclusion – 7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand
Demand is the want for a product backed by the purchasing power. When price changes there is a change in quantity demanded also. Law of demand states that when the price of a product decreases the quantity demanded increases. In the market economy, the prices of goods and services are decided by the market forces. Income, price affect the law of demand. As a result, any change in the factors will cause the demand to change. At the same time, there are exceptions to the law of demand too.
Law of demand is caused by the substitution effect, income effect and other factors. As a result due to the law of demand, the demand curve is downward sloping. Demand is a broad concept overall. And demand forms a major market force in the economy.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
2 Replies to “7 Minutes Guide To The Law of Demand”