Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction that is derived from consuming an additional unit of a commodity or service. Therefore, it implies that the utility derived from that additional unit is inversely proportional to the number of units he already consumed. MU explains the fundamental economic reality of price in the economy. Economists believe that the price is partly determined by the commodity’s utility. Therefore the degree of satisfaction derived from the commodity is directly proportional to the price. In this section, we will also study law of diminishing marginal utility. Along with that we will see the marginal utility formula.

MU theory examines the satisfaction gained by the consumer from consuming an extra unit of that commodity. Utility is the satisfaction that derived after consuming a commodity or a service. But marginal utility is the benefit derived after consuming an extra unit of the good or service. Utility is not a constant concept. Utility keeps on decreasing when additional units of the commodity are consumed. It can be positive, zero or negative. Now, let us see the marginal utility formula along with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
HIGHLIGHTS
Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that is gained by the consumer after consuming an additional unit of a good or service.
UNDERSTANDING MARGINAL UTILITY
Economists study MU to sense how satisfaction levels of the consumer affect their decision. Satisfaction gained after consuming a commodity affects the decision making process of the consumer. As a result, they tend to consume more units of that product. But in cases after consuming a certain unit of the product the utility derived begins to decline. The law of diminishing marginal utility is developed. It studies that after consumption of the first unit of the commodity the later units have lesser utility.
HIGHLIGHTS
Marginal utility tends to decrease. But it will not be zero depending on the type of the product consumed.
The concept of marginal utility explains how consumers make decisions to get the maximum benefit in their limited budget. Consumers will continue consuming the product till the marginal utility is greater than the marginal cost. In the market, marginal cost is equal to the price of the goods and service available. Thus, people keep on consuming until the marginal utility falls to the price of the commodity.
HISTORY
In the 18th century, Adam Smith discussed the “paradox of water and diamond”. This paradox explains that the value of diamond is higher than water. But water is essential to sustain human life. The concept of MU was developed to explain the economic reality of price. The economic reality of price is driven by the utility of the product.

In the 1870s economist William Stanley Jevons, Carl Menger and Leon Walras came to the conclusion that marginal utility is the answer to the “Water Diamond Paradox”. Jevons in his book, “The Theory of Political Economy” explained that economic decisions are made on MU and not on total utility.
HIGHLIGHTS
William Stanley Jevons, Carl Menger and Leon Walras developed the concept of marginal utility.
TYPES OF MARGINAL UTILITY
MU is of multiple types. The most important three types of MU are:

Positive Marginal Utility
MU is positive when consuming more goods and services bring additional satisfaction/happiness. Eating a pack of ice-cream will have a utility but having an extra pack will increase the utility. Therefore the extra pack will make you feel better. Therefore, the utility derived in positive.
Zero Marginal Utility
Zero MU is derived when consuming an extra quantity of the commodity does not bring an extra amount of satisfaction. For example, after completing the two packs of ice-cream your stomach is full. You are not willing to consume another pack of the ice-cream. But still you consume another pack of the product. You do not get any satisfaction from consuming it. Therefore, in this case, the utility is zero.
Negative Marginal Utility
Negative MU is derived when consuming an extra amount of the good or service is harmful. It will harm the consumer in some way or the other. For example, after completing the third pack of ice-cream you know that if you consume one more pack you will catch cold/fall sick. In this case, the MU is negative.
RELATION BETWEEN TOTAL UTILITY AND MARGINAL UTILITY
Total utility is the summation of marginal utility and MU is the change in the total utility. Total utility is always positive. But MU may be positive, negative or zero.
When MU is positive, total utility is increasing but at a diminishing rate. MU becomes zero, the total utility is maximum. When MU is negative, the total utility is decreasing.

MARGINAL UTILITY FORMULA
The marginal utility can be represented as the change in total utility divided by change in units. The marginal utility formula can be represented as:
Marginal Utility = Change in Total Utility/Change in Units
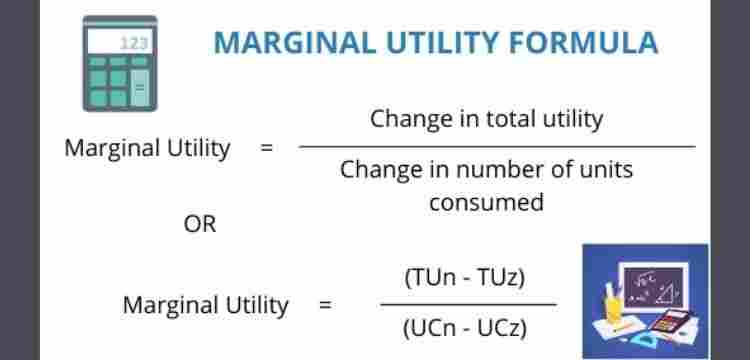
The change in total utility can be calculated as the current minus the previous total utility. Change in units is the current minus the previous units.
LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as consumption increases the utility derived after consuming each additional unit declines. Utility of the product changes. Since consumption of additional units take place. Utility in economics represents satisfaction/happiness. Marginal utility is the increase in utility after consuming an additional unit of a commodity.
HIGHLIGHTS
The law states that as consumption increases the marginal utility derived after consuming each additional unit declines.
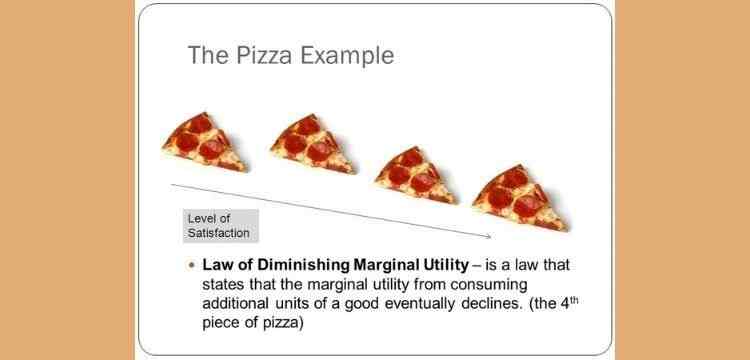
The law of diminishing marginal utility is an important concept in economics. It represents the tendency of human behaviour. When a consumer increases the consumption of a good or service, there is a decline in utility after each successive unit. In other words, more the consumption level, less will be the utility. For example, when a person is hungry, he decides to have a burger. After consuming the first burger, he will get the maximum satisfaction. If he consumes the second burger, the utility/satisfaction derived will be less than the earlier level. In this way, the more the consumption level increases, the utility level keeps on decreasing.
ASSUMPTIONS
The assumptions of the law of diminishing marginal utility are:

Standard Unit
The law of diminishing marginal utility assumes that there must be a standard unit for consumer goods. For example, a glass or milk, a plate of rice etc.
Taste and Preference
The law of diminishing marginal utility assumes that the consumer taste and preference to be the same during the consumption period. If the consumer taste and preference change then the law will not hold.
Continuity in Consumption
The law assumes that the consumption should be continuous. In other words, the time interval between the consumptions of the commodity should be short.
Reasonability
The law implies that the commodity consumed should be of standard size. If the standard unit of water is glass, then the standard unit should not be replaced. For example, the glass of water replaced with a spoon of water.
Suggested Blog:
7 Minutes Guide to Law of Demand
Monetary Policy: Learn in 5 Minutes
LIMITATIONS
The law of diminishing utility helps the consumers to decide their expenditure. Some of the limitations associated with this law are:

Unrealistic Assumptions
The assumptions of the law of diminishing utility are unrealistic. The assumption of continuity and homogeneity is not possible to find at once.
Not applicable
There are certain goods and services on which the law of diminishing utility is not applicable. The consumption of those goods and services in the economy is not regular/continuous. Therefore, continuity is not there.
Constant Marginal Utility of Money
The law assumes that the MU of money to be constant. But the assumption of constant MU is unrealistic. The MU of money is always on a decline.
EXCEPTIONS
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as units of goods and services increase, the utility derived falls. However, there are certain exceptions to the law.
Hobbies
Hobbies do not follow the law of diminishing returns. The satisfaction level of the person increases when he is practising his hobby. For example, a person has the hobby to collect stamps. So if there is a new stamp, his satisfaction level will rise when he collects that new stamp. Therefore, the utility has not declined after each passing level. Thus, this point is an exception to the rule.
Misers
The law of diminishing returns does not hold true for misers. The utility derived after each consumption level increases with every increasing quantity. Therefore, the utility derived is high for misers.
CONCLUSION
The marginal utility is a very important concept in microeconomics. Utility is a term that depicts satisfaction/happiness. In this blog we have seen the key points of utility. The law of diminishing returns is also an important part of the broad topic. Diminishing returns is where the utility of consuming a commodity declines after every unit of that commodity consumed. We have also seen the marginal utility formula. With respect to that we have seen the assumptions, limitations and exceptions of the law of diminishing marginal utility.

 WhatsApp
WhatsApp